What is Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
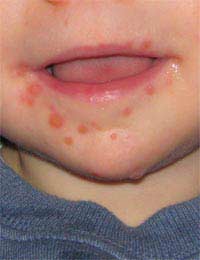
Although this illness sounds like something more likely to affect pigs and cattle than humans, hand foot and mouth disease is actually a common childhood infection that will clear up on its own.
Most common in children aged 10 years old and younger, it occasionally affects older children and even adults. It gets its name from tiny little sores or spots that usually develop first of all in the mouth, then spread to the hands and the soles of the feet.
The illness is contagious and symptoms first appear about three to five days after having contact with someone who has it. Hand, foot and mouth disease is not a lot of fun, but it goes away fairly quickly and almost never causes any complications at all.
Symptoms of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
Parents may notice the symptoms of the disease first when small white spots, almost resembling canker sores, appear in their child’s mouth. Very quickly they will appear as a rash on the hands and feet, and sometimes they spread up the backs of the legs, on the bottom and even on the genital area.The spots look almost like chicken pox, but they are not usually itchy. In some cases, however, they can be very tender. Your child may lose his appetite if he has many sores in his mouth, and some children have a sore throat and feel generally unwell.
A mild fever also occasionally accompanies hand, foot and mouth disease, and if it gets quite high, you may want to visit the doctor. Often, however, a doctor’s visit may be unnecessary, as there is little to be done with hand, foot and mouth disease except wait it out.
Causes of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
Several viruses can be responsible for this infection, and the virus that caused it may make the symptoms more or less tolerable. Most cases are caused by what is known as the coxsackie virus A16, which is a type of enterovirus. Adults who come down with it usually have very mild symptoms.As mentioned, the infection is very contagious, especially during the first few days, so you may be advised to keep your child away from other children at this time. Also, the virus can stay in faeces for up to four weeks, so if your child catches it they should be extra vigilant when it comes to hand washing after using the toilet during this time.
Complications are very rare, but occasionally hand, foot and mouth disease can lead to mild cases of viral meningitis. It is much less severe than bacterial meningitis, with the vast majority of people catching it making a complete recovery within a fortnight.
Treatment of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease does not really require treatment; what it requires is extra care to make the patient more comfortable. Do the usual things when someone has a mild fever or feels unwell – keep them cool and give them plenty to drink, as well as paracetamol or ibuprofen. If in doubt, consult your doctor.Also, keep in mind that if your child scratches the sores or spots there is a chance they could become infected, which sometimes will require antibiotics.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common childhood illness that involves spots or sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet, which can be itchy and tender. The illness usually lasts about seven to ten days, then goes away on its own. There is no real treatment: just make the patient comfortable and it should go away within ten days.

Re: Identifying and Treating Contact Dermatitis
Hello and Good Day! I have completed an audit of your website, and I would like to share it with you. This…
Re: Identifying and Treating Contact Dermatitis
Hello and Good Day I am Aditya Business Development Manager with a reputable online marketing company based in…
Re: Why Changing Shampoos Regularly Might Harm You
I suffered really badly with post partum hairloss. I lost almost half the hairs on my head. I use good…
Re: Why Changing Shampoos Regularly Might Harm You
I have oily scalp and dry ends. I have been using dove intense repair from last 1 year. I had no issues…
Re: Why Changing Shampoos Regularly Might Harm You
I used dove from last one year its sometime give hairfall nd sometime not thn i switch to sunsilk long nd…
Re: Why Changing Shampoos Regularly Might Harm You
I was using head and shoulders for over 10 years and I always lost a lot of hair. My hair is very thin. I…
Re: Dealing With Seborrheic Keratoses
I have a sebbhoraic keratosis directly under my left eye. It is slowly growing and is currently about almost a centimetre in…
Re: Identifying and Treating Contact Dermatitis
First page rankings on Google We can put your website on 1st page of Google to drive relevant traffic to…
Re: Dealing With Seborrheic Keratoses
It may be interesting to add that seborrheic keratoses might herald certain gastrointestinal malignancies. It's called the…
Re: Medical Treatments for Help With Psoriasis
Wife has all 3 types of Psoriasis and Psoriasis arthritis but cannot get the Apremilast as NICE say she not…